Python `While`循环
Python While循环
Python While循环允许执行部分代码,直到给定条件返回 false。它也被称为预测试环路。
它可以被看作是一个重复的 if语句。当我们不知道迭代次数时,While循环是最有效的。
语法如下。
while expression: |
这里,语句可以是单个语句或一组语句。表达式应该是任何导致真或假的有效 Python 表达式。true 是任何非零值,false 是 0。
当循环流程图
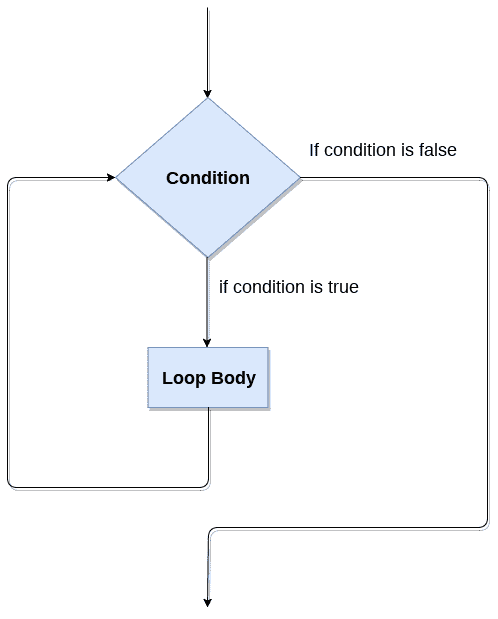
循环控制语句
我们可以在使用循环控制语句执行循环时改变的正常顺序。当 While循环执行完成时,该范围内定义的所有自动对象都将被拆除。Python 提供了以下控制语句在 While循环中使用。
1.continue语句-
当遇到 continue语句时,控制转移到循环的开始。让我们理解下面的例子。
示例:
# prints all letters except 'a' and 't' |
输出:
Current Letter : j |
2.break语句-
当遇到 break语句时,它会将控制带出循环。
示例:
# The control transfer is transfered |
输出:
Current Letter : j |
3.pass语句-
pass语句用于声明空循环。它也用于定义空类、函数和控制语句。让我们理解下面的例子。
示例-
# An empty loop |
输出:
Value of i : 10 |
示例-1:
使用 While循环打印 1 到 10 的程序
i=1 |
输出:
1 |
示例 2:
打印给定数字表的程序。
i=1 |
输出:
Enter the number:10 |
无限 While循环
如果 While循环中给出的条件永远不会变为假,那么 While循环永远不会终止,变成无限 While循环。
While循环中的任何非零值表示始终为真条件,而零表示始终为假条件。如果我们希望我们的程序在没有任何干扰的情况下连续运行,这种方法是有用的。
例 1
while (1): |
输出:
Hi! we are inside the infinite while loop |
例 2
var = 1 |
输出:
Enter the number:10 |
将 else 与 While循环一起使用
Python 允许我们在 While循环中使用 else 语句。当 while 语句中给出的条件变为 false 时,执行 else 块。就像循环一样,如果 While循环使用 break语句中断,那么 else 块将不会被执行,而 else 块之后的语句将被执行。else 语句可以选择与 While循环一起使用。考虑下面的例子。
例 1
i=1 |
例 2
i=1 |
输出:
1 |
在上面的代码中,当遇到 break语句时,While循环停止执行并跳过 else 语句。
示例-3
打印斐波那契数列到给定极限的程序
terms = int(input("Enter the terms ")) |
输出:
Enter the terms 10 |












