Python 数据类型
Python 数据类型
变量可以保存值,每个值都有一个数据类型。Python 是一种动态类型语言;因此,我们在声明变量时不需要定义它的类型。解释器隐式地将值与其类型绑定。
a = 5 |
变量 a 保存整数值 5,我们没有定义它的类型。Python 解释器会自动将变量 a 解释为整数类型。
Python 使我们能够检查程序中使用的变量的类型。Python 为我们提供了 type() 函数,返回传递的变量的类型。
考虑以下示例来定义不同数据类型的值并检查其类型。
a=10 |
输出:
<type 'int'> |
标准数据类型
一个变量可以保存不同类型的值。例如,一个人的名字必须存储为字符串,而他的 id 必须存储为整数。
Python 提供了各种标准数据类型,定义了每种类型的存储方法。下面给出了 Python 中定义的数据类型。
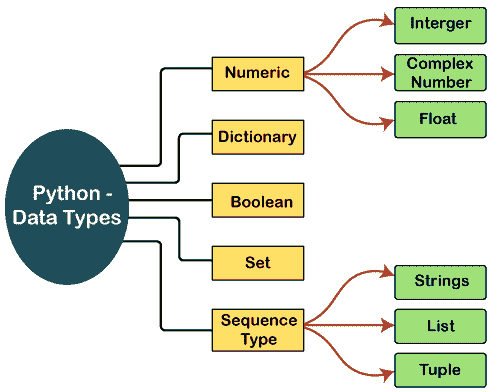
在教程的这一部分,我们将简要介绍上述数据类型。我们将在本教程的后面详细讨论每一个。
Numbers
Number 存储数值。整数、浮点和复数值属于 Python Numbers 数据类型。Python 提供了 type() 函数来知道变量的数据类型。类似地, isinstance() 函数用于检查某个对象是否属于某个特定的类。
当一个数字被分配给一个变量时,Python 会创建数字对象。比如;
a = 5 |
输出:
The type of a <class 'int'> |
Python 支持三种类型的数字数据。
Int - 整数值可以是任意长度,如整数 10、2、29、-20、-150 等。Python 对整数的长度没有限制。其价值属于国际
Float - Float 用于存储 1.9、9.902、15.2 等浮点数。它精确到小数点后 15 位。
复数- 复数包含有序对,即 x + iy,其中 x 和 y 分别表示实部和虚部。2.14j、2.0 + 2.3j 等复数。
SequenceType
Strings
字符串可以定义为引号中表示的字符序列。在 Python 中,我们可以使用单引号、双引号或三引号来定义字符串。
Python 中的字符串处理是一项简单的任务,因为 Python 提供了内置函数和运算符来执行字符串中的操作。
在字符串处理的情况下,运算符+用于连接两个字符串,因为操作*“hello”+“python”返回“hello python”*。
运算符被称为重复运算符,因为操作“Python” 2 返回“Python Python”。
以下示例说明了 Python 中的字符串。
示例- 1
str = "string using double quotes" |
输出:
string using double quotes |
考虑下面的字符串处理示例。
示例- 2
str1 = 'hello javatpoint' #string str1 |
输出:
he |
List
Python 列表类似于 c 语言中的数组。但是,列表可以包含不同类型的数据。列表中存储的项目用逗号(,)分隔,并括在方括号[]内。
我们可以使用 slice [:]运算符来访问列表的数据。串联运算符(+)和重复运算符(*)处理列表的方式与处理字符串的方式相同。
考虑下面的例子。
list1 = [1, "hi", "Python", 2] |
输出:
[1, 'hi', 'Python', 2] |
Tuple
元组在许多方面类似于列表。像列表一样,元组也包含不同数据类型项的集合。元组的项用逗号(,)分隔,并包含在括号()中。
元组是只读的数据结构,因为我们不能修改元组的项目的大小和值。
让我们看一个简单的元组例子。
tup = ("hi", "Python", 2) |
输出:
<class 'tuple'> |
Dictionary
字典是项的键值对的无序集合。它就像一个关联数组或哈希表,其中每个键存储一个特定的值。键可以保存任何原始数据类型,而值是任意的 Python 对象。
字典中的项目用逗号(,)分隔,并包含在大括号{}中。
考虑下面的例子。
d = {1:'Jimmy', 2:'Alex', 3:'john', 4:'mike'} |
输出:
1st name is Jimmy |
Boolean
布尔类型提供两个内置值,真和假。这些值用于确定给定语句的真假。它由类 bool 表示。True 可以用任何非零值或“T”表示,而 false 可以用 0 或“F”表示。考虑下面的例子。
# Python program to check the boolean type |
输出:
<class 'bool'> |
Set
Python 集是数据类型的无序集合。它是可迭代的、可变的(可以在创建后修改),并且具有独特的元素。在 set 中,元素的顺序是未定义的;它可以返回元素的改变的序列。通过使用内置函数 **set(),**创建集合,或者在花括号中传递一系列元素,并用逗号分隔。它可以包含各种类型的值。考虑下面的例子。
# Creating Empty set |
输出:
{3, 'Python', 'James', 2} |












