Python 日期和时间
Python 日期和时间
Python 为日期时间模块提供了真实的日期和时间。在现实应用中,我们需要处理日期和时间。Python 使我们能够安排我们的 Python 脚本在特定的时间运行。
在 Python 中,日期不是数据类型,但是我们可以通过导入以日期时间、时间和日历命名的模块来处理日期对象。
在教程的这一部分,我们将讨论如何在 Python 中使用日期和时间对象。
日期时间类别分为六个主要类别。
date -它由年、月和日作为属性组成。
time -这是一个完美的时间,假设每天都有精确的 246060 秒。它有小时、分钟、秒、微秒和 tzinfo 属性。
datetime -它是日期和时间的分组,以及年、月、日、小时、分钟、秒、微秒和 tzinfo 属性。
timedelta- 它表示两个日期、时间或日期时间实例到微秒分辨率之间的差异。
tzinfo -提供时区信息对象。
datetime- 包含在新版 Python 中。它是实现 tzinfo 抽象基类的类。
滴答声
在 Python 中,时间瞬间是从 1970 年 1 月 1 日上午 12 点开始计算的。模块时间的函数 time() 返回自 1970 年 1 月 1 日上午 12 点以来总数。刻度可以看作是测量时间的最小单位。
考虑以下示例
import time; |
输出:
1585928913.6519969 |
如何获取当前时间?
时间模块的 localtime()函数用于获取当前的时间元组。考虑下面的例子。
例
import time; |
输出:
time.struct_time(tm_year=2020, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=3, tm_hour=21, tm_min=21, tm_sec=40, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=94, tm_isdst=0) |
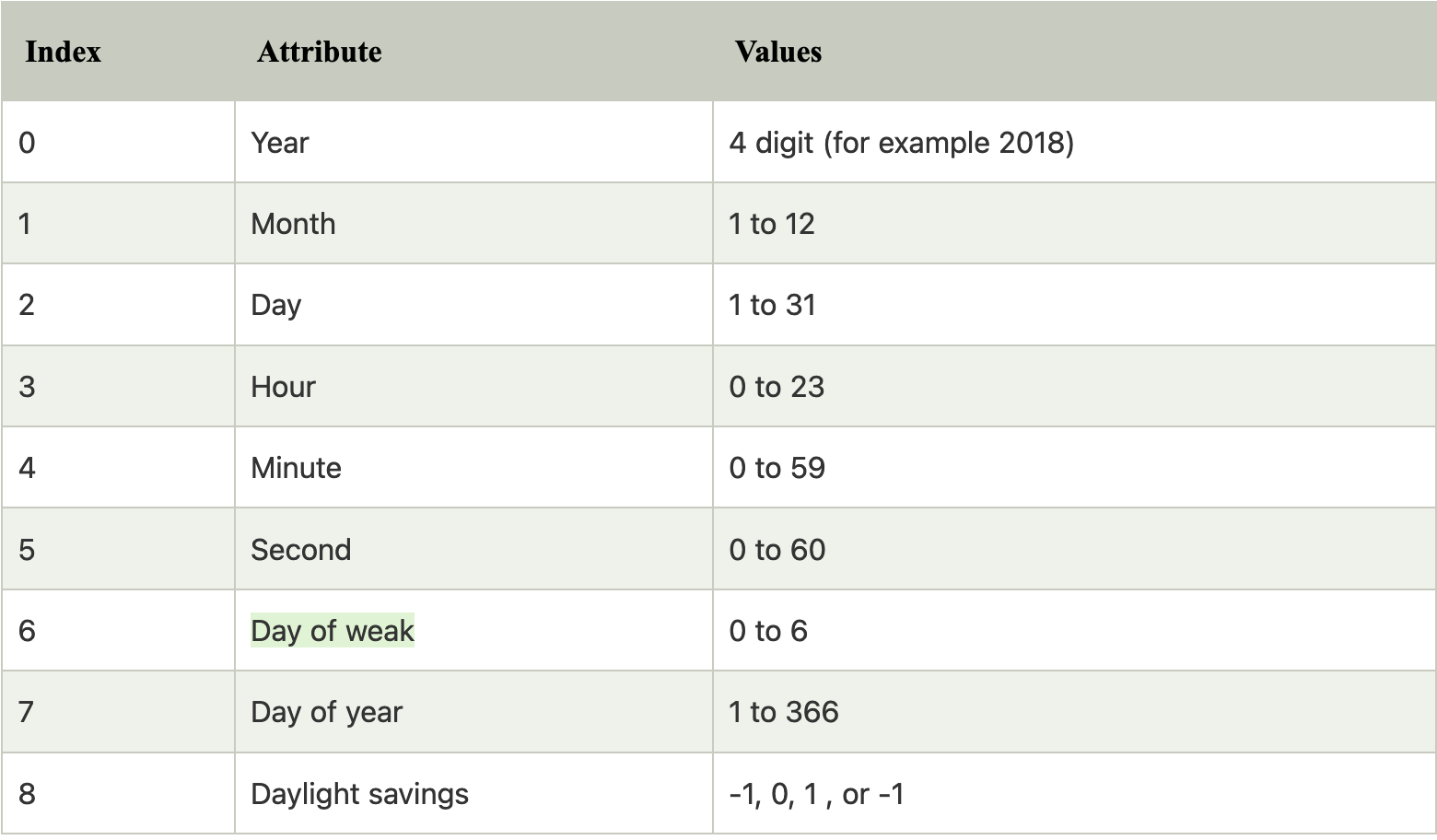
时间元组
时间被视为 9 个数字的元组。让我们看看时间元组的成员。
获取格式化时间
可以使用时间模块的 asctime() 功能格式化时间。它返回正在传递的时间元组的格式化时间。
例
import time |
输出:
Tue Dec 18 15:31:39 2018 |
Python 睡眠时间
时间模块的 sleep() 方法用于在给定的时间内停止脚本的执行。输出将延迟作为浮点提供的秒数。
考虑下面的例子。
例
import time |
输出:
0 |
日期时间模块
日期时间模块使我们能够创建自定义日期对象,对日期执行各种操作,如比较等。
要使用日期作为日期对象,我们必须将datetime模块导入 python 源代码。
考虑以下示例来获取当前时间的日期时间对象表示。
例
import datetime |
输出:
2020-04-04 13:18:35.252578 |
创建日期对象
我们可以在日期时间构造器中绕过需要创建日期对象的日期来创建日期对象。
考虑下面的例子。
例
import datetime |
输出:
2020-04-04 00:00:00 |
我们还可以指定创建 datetime 对象的时间和日期。考虑下面的例子。
例
import datetime |
输出:
2020-04-04 01:26:40 |
在上面的代码中,我们以顺序的方式传入了 datetime() 函数年、月、日、小时、分钟和毫秒属性。
两个日期的比较
我们可以使用比较运算符如>、> =、
考虑下面的例子。
例
from datetime import datetime as dt |
输出:
fun hours |
日历模块
Python 提供了一个日历对象,其中包含各种使用日历的方法。
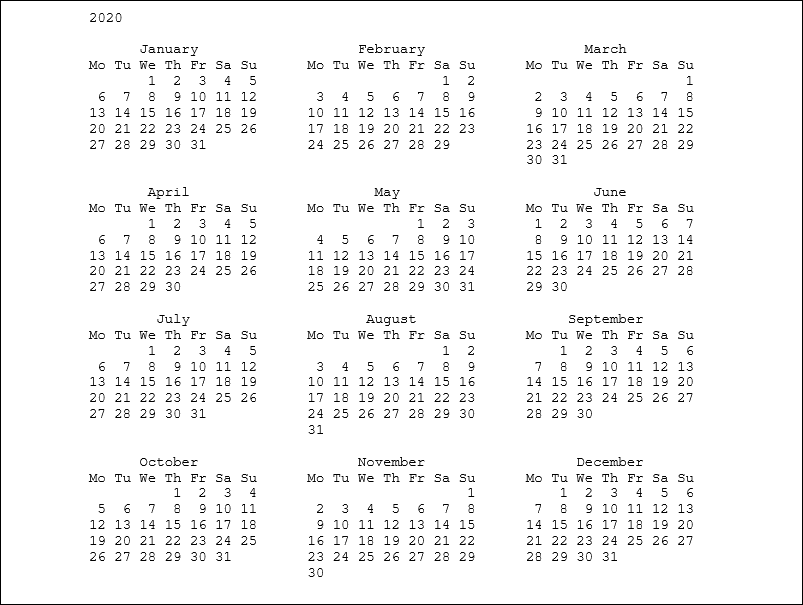
考虑以下示例来打印 2018 年最后一个月的日历。
例
import calendar; |
输出:
March 2020 |
打印全年日历
日历模块的 prcal()方法用于打印全年的日历。要打印日历的年份必须传递到此方法中。
例
import calendar |
输出: